|
To aid in the replacement of the 40 mm mountings, the GWS-21 version was actually controlled by the Type 262 Radar gun control used by the 40 mm Bofors. GWS-22 uses a modified director based upon the MRS-3 (the British version of the Mark 56 FCS). GWS-24 employs the WSA-4 FCS. Sea Cat is mounted on a 4 round trainable launcher. Reloading is by hand, carrying missiles by trolley from the magazine. There was also a lightweight 3 round version for small ships. The missile proved accurate, reliable
and cheap and 7 other countries have used it, although it has been replaced
in Royal Navy service by the Sea Dart and Sea Wolf.
|
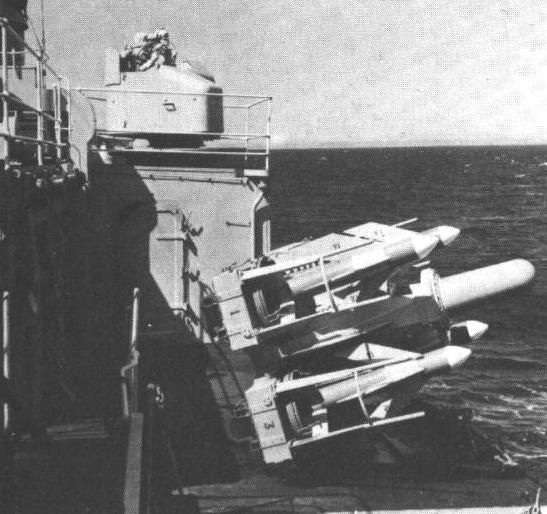

Quad Sea Cat launcher with original visual
director
|
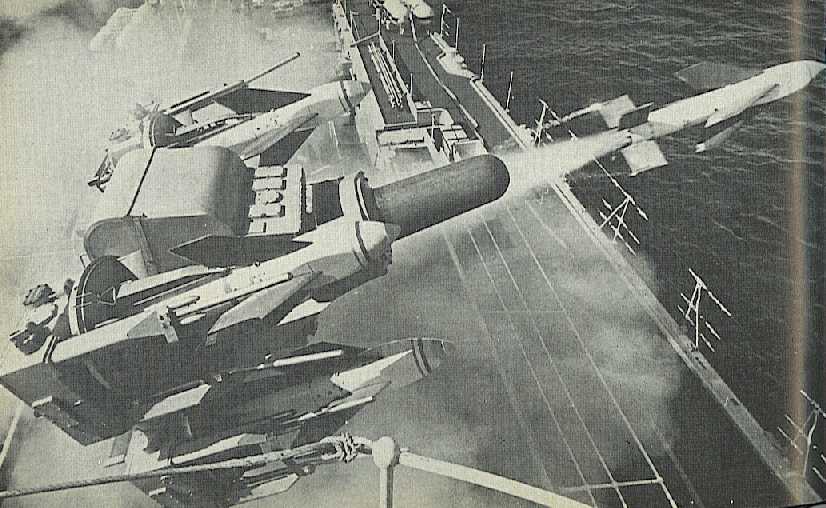
SeaCat Launcher |