|
The four Myôkô class cruisers conducted AA trials with these guns in 1931. Steaming at 18 knots and using the the Type 89 HA computer, the cruisers scored 2.2% hits against aerial targets towed at 60 to 70 knots at altitudes of 1,500 to 2,000 m (4,900 to 6,600 feet). Firing was at an average of 6.4 rounds per minute at ranges between 2,000 and 5,500 m (2,200 and 6,000 yards). The carrier Kaga and those cruisers modernized during the late 1930s had these weapons replaced by the 12.7 cm/40 (5") Type 89 AA gun. However, Akagi carried them to her end at Midway. The earlier guns were of built-up construction but the later ones were of monobloc construction. All used a semi-automatic sliding breech-block mechanism. A total of about 3,000 guns were manufactured, with 2,320 (one source says 2,152) of them being produced between 1942 to 1945. |
12 cm/45 (4.7") guns on Heavy Cruiser IJN
Nachi
|
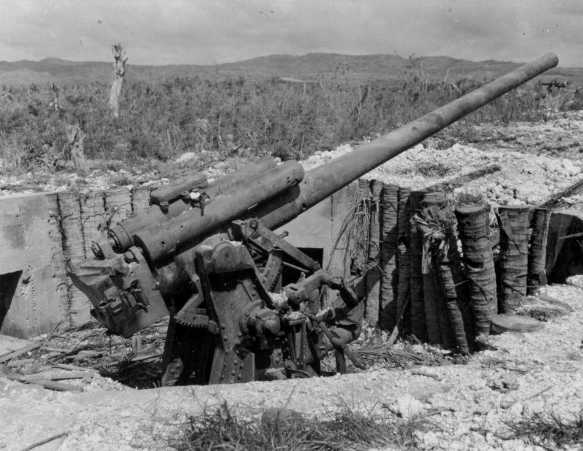

12 cm/45 (4.7") gun captured on hill east
of the Orote Peninsula Airfield, Guam
|
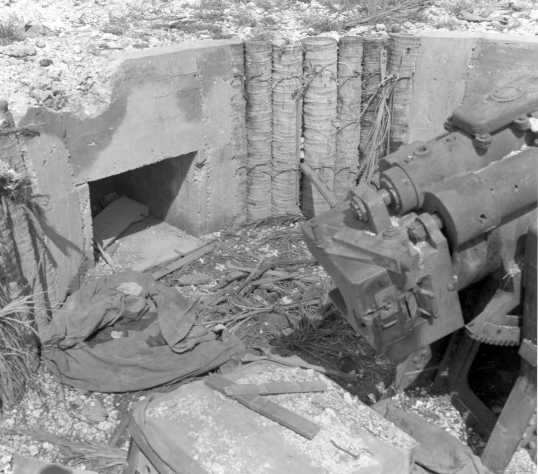

Breech of above weapon
|